While many countries around the world are gradually shifting away from coal as a primary energy source, Pakistan is considering coal as a potential immediate solution to its ongoing energy crisis.
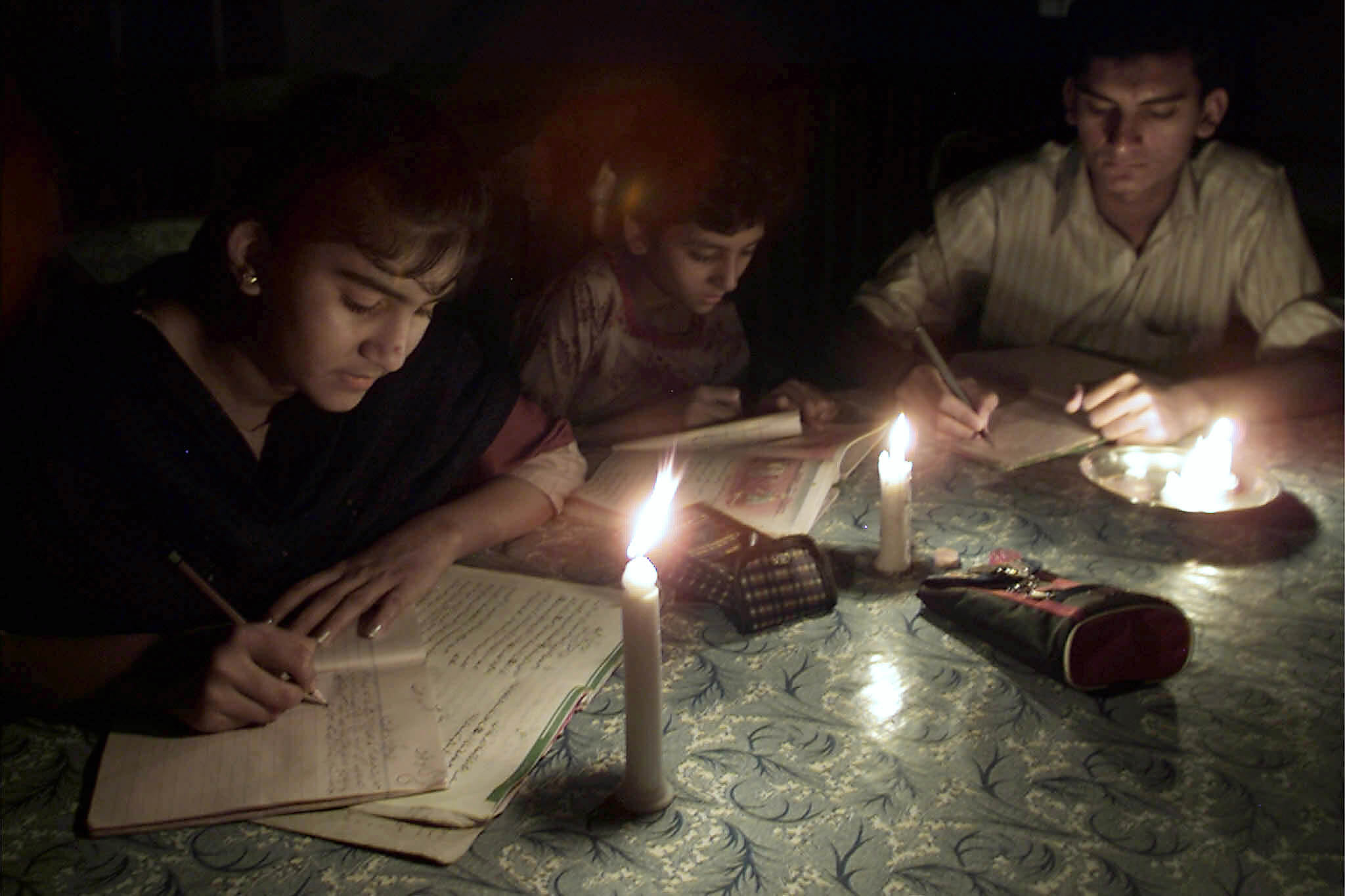
Pakistan has been facing frequent power shortages, leading to economic strain. The recent discovery of extensive coal deposits in the Tharparkar district offers a significant opportunity for the country. The exploration of Pakistan’s first open-pit coal mine is seen as a potential remedy to the long-standing energy challenges faced by the nation.
The newfound coal reserve has sparked enthusiasm among local residents who are gearing up for new employment opportunities in the mining industry. However, this shift towards coal contradicts the global trend towards renewable energy sources. While coal is criticized for being non-renewable, detrimental to personal health, and a major contributor to carbon emissions and climate change, it remains a cost-effective, reliable energy source. The coal reserves in Thar have the potential to power Pakistan for up to a century.
As part of the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), China has invested in 21 energy projects in Pakistan, with a focus on coal-based initiatives. The CPEC initiative also includes projects in solar, wind, and hydro energy. Despite the worldwide move away from coal, the vast coal reserves in Tharparkar present a unique opportunity for Pakistan to address its energy crisis without heavy reliance on external imports.
The reliance on imported energy sources has hindered Pakistan’s economic progress in various sectors. Therefore, tapping into the Tharparkar coal reserves could potentially provide a solution to many of the economic challenges faced by the country.